The Great Depression, which began with the stock market crash of 1929, was one of the most severe economic downturns in modern history. Spanning almost a decade, it profoundly changed the financial landscape of the United States and the world. Millions of people faced unemployment, businesses closed their doors, and families struggled to make ends meet, leading to lasting social and psychological effects. The responses of governments and institutions during this tumultuous period shaped the policies and regulations of the present day. This article seeks to explore the multifaceted history of the Great Depression, examining its causes, consequences, and the pivotal lessons learned from this challenging period in American history.
Causes of the Great Depression
The Great Depression did not strike spontaneously; rather, it was the result of a complex interplay of multiple factors that converged to create an environment ripe for financial disaster. One of the primary causes was the stock market crash that occurred on October 29, 1929, commonly referred to as Black Tuesday. This event prompted widespread panic as investors rapidly sold off stocks, leading to a drastic drop in stock prices. However, the roots of the Great Depression extend beyond this dramatic event.
Beyond the stock market turmoil, the 1920s—often dubbed the “Roaring Twenties”—was characterized by speculative investment and excessive risk-taking behavior. Many investors bought stocks on margin, borrowing money to purchase more shares than they could afford. When the market began to decline, these margins became unsustainable, leading to massive sell-offs that accelerated the decline. This heavy reliance on speculation created an unsound financial system, undermining confidence in the market.
Additionally, the banking system’s weaknesses played a significant role in triggering the economic crisis. Many banks had overextended themselves through risky loans, particularly in real estate. When the stock market crashed, many banks were unable to recover their debts, leading to a cascade of bank failures. As banks closed their doors and depositors rushed to withdraw their savings, the banking system became increasingly unstable, further deepening the economic crisis.
International trade tensions and protectionist policies also contributed to the downturn. Following the stock market crash, the United States implemented the Smoot-Hawley Tariff in 1930, which significantly raised tariffs on imported goods. This policy aimed to protect domestic industries but backfired as foreign nations retaliated with their own tariffs. The result was a dramatic decline in international trade, exacerbating the economic malaise experienced both in the U.S. and worldwide.
Furthermore, agricultural overproduction in the 1920s led to plummeting prices for farmers. The Dust Bowl, a severe drought that affected the Great Plains in the 1930s, further devastated agriculture and displaced thousands of families, adding to the economic despair. Many farm families migrated to cities in search of work, only to find unemployment and limited opportunities.
Finally, the lack of a coordinated international response to economic troubles also played a role. As nations faced their own financial struggles, the absence of effective international cooperation led to an environment of isolationism and a reluctance to implement necessary reforms.
In conclusion, the Great Depression was a multifaceted phenomenon with roots in financial speculation, banking failures, protectionist policies, agricultural decline, and inadequate international response. Understanding these causes is vital for analyzing the subsequent consequences and lessons learned from this historical period.
The Great Depression’s economic consequences
The economic ramifications of the Great Depression were severe and far-reaching. Unemployment rates skyrocketed, reaching nearly 25% in the United States at the height of the crisis. This staggering figure represents millions of individuals and families who lost their sources of income, casting a pall over the entire economy. As businesses shuttered and industries collapsed, the consequences extended well beyond the immediate loss of jobs; the foundations of the economy were shaken to their core.
The impact on commerce was equally dire. Banks failing resulted in the disappearance of individuals’ savings and further reductions in consumer spending. With people lacking confidence in the financial system, many chose to hoard cash rather than spend it, leading to deflation—a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. As businesses saw their revenues dwindle, they were forced to cut costs, which often meant layoffs and wage reductions. This vicious cycle perpetuated the economic downturn, as decreased spending led to further business closures, resulting in even more unemployment.
The agricultural sector was particularly hard hit during the Great Depression. Farmers, already struggling with debts from overproduction and falling prices, faced additional challenges as drought conditions in the Dust Bowl destroyed crops and pastures. Agricultural prices plummeted, and many farmers were unable to meet mortgage payments or cover living expenses. This led to widespread foreclosures on farms, resulting in massive dislocation of farming families—many of whom migrated towards California and other states in search of work.
The effects of the Great Depression were not isolated to the United States but were felt worldwide. Many countries experienced economic downturns in tandem with the U.S., creating a global economic crisis. This situation was exacerbated by interconnected economies, where the economic struggles of one nation rippled through international markets. Import and export rates plummeted, and countries were unable to revive their economies without cooperation or assistance from others.
In response to the economic turmoil, governments began to implement relief and recovery programs, such as the New Deal initiated by President Franklin D. Roosevelt. This marked a significant shift in government involvement in the economy and laid the groundwork for future economic policies. However, these efforts were often met with resistance and skepticism. The effectiveness of government intervention was debated, evaluating its role in addressing or prolonging the economic hardships.
Ultimately, the economic consequences of the Great Depression reshaped the financial landscape. Innovations in labor protections, social security systems, and federal regulations aimed at stabilizing the economy were introduced as a direct response to the financial crisis. These measures would pave the way for future economic reforms worldwide.
Social effects on American society
The Great Depression had profound and lasting effects on American society, transforming the very fabric of social interactions, community structures, and family dynamics. In the wake of financial collapse, the impact of widespread unemployment, poverty, and hardship rippled through every class and demographic, altering how individuals and families navigated their daily lives.
One of the most immediate social ramifications of the Great Depression was the staggering rise in unemployment. As businesses closed and jobs vanished, millions of Americans found themselves out of work. The psychological toll of unemployment was significant. For many, work had represented not just a source of income but also a sense of identity and purpose. The inability to provide for one’s family fostered feelings of shame and despair, leading to a rise in mental health issues, including depression and anxiety.
Family dynamics were also profoundly affected. In many cases, traditional roles were upended, with men—the primary breadwinners—struggling to find work and women increasingly stepping into roles as wage earners. Some women took on domestic work, while others sought employment in factories or other sectors that were less severely impacted by the downturn. The need for dual-income households, although often challenging, began to shift societal expectations around gender roles and responsibilities. As a result, there was a gradual transformation in perceptions of women’s work and capabilities during and after the Great Depression.
Communities across the country banded together during this tumultuous time, forming support networks to assist those in need. Mutual aid societies, food banks, and community organizations emerged to help families facing hunger and poverty. Neighborly cooperation became a crucial means of survival; however, it also illustrated the social fractures becoming apparent. Ethnic and racial minorities, particularly African Americans and immigrants, often faced disproportionate challenges due to systemic discrimination in accessing employment and government assistance. This inequity laid bare the longstanding racial divides within American society.
Furthermore, the Great Depression had a lasting impact on the education of children and young adults. Financial hardships led many families to withdraw their children from school to contribute to work. Poverty-stricken families were often unable to afford basic school supplies, leading to diminished educational opportunities for the youth. Such disruptions had long-lasting consequences, hindering the ability of future generations to achieve upward mobility.
Cultural expressions during the Great Depression also evolved, reflecting the prevailing moods of despair, hope, and resilience. Art, literature, and music from this period captured the struggles, aspirations, and daily realities of the American populace. A notable cultural response was the Federal Art Project initiated as part of the New Deal, which aimed to provide jobs for artists while making art accessible to the general public. Similarly, the themes of folk music and the emergence of socially conscious literature resonated with those grappling with their own hardships.
Ultimately, the Great Depression left an indelible mark on American society. The experiences of this period fostered a collective consciousness that influenced values regarding community, government responsibility, and economic security. The lessons learned from this era would continue to shape societal attitudes towards the economy and social welfare in the decades to come.
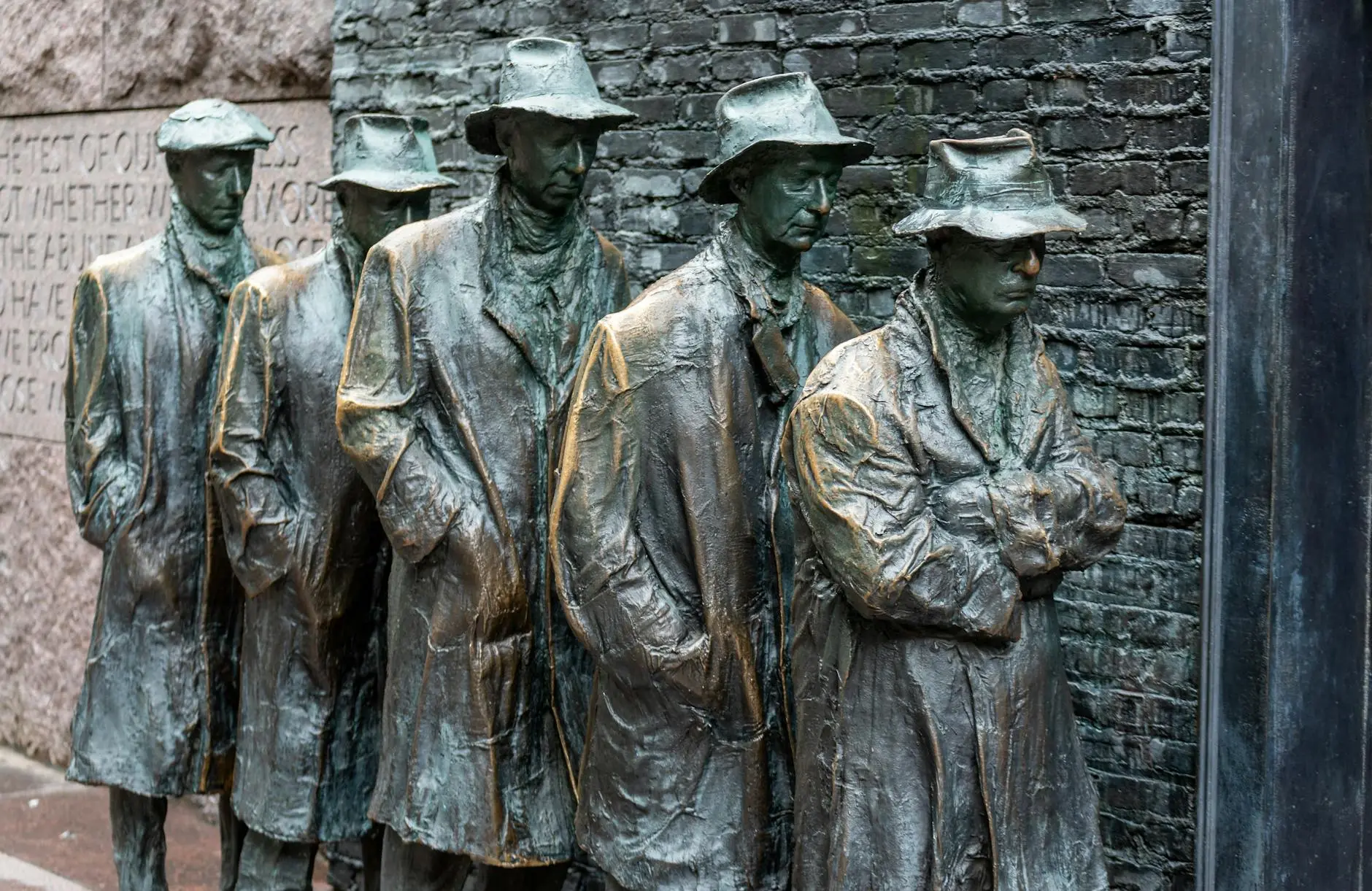

Government response to Great Depression and reform
The Great Depression precipitated a significant transformation in the relationship between the American government and its citizens. Faced with unprecedented economic hardship, governmental responses evolved from initial inaction to a series of proactive measures aimed at alleviating suffering and stimulating recovery. President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s New Deal emerged as the cornerstone of this response, redefining the role of the federal government in addressing economic and social challenges.
Initially, the government’s response to the onset of the Great Depression was marked by hesitation and limited interventions. President Herbert Hoover, who assumed office just before the crash, believed in limited government involvement in the market, adhering to the principles of laissez-faire economics. His administration’s efforts to stimulate the economy through voluntary cooperation with businesses were largely ineffective, resulting in widespread frustration among the populace as conditions worsened.
Recognizing that more aggressive intervention was necessary, Franklin D. Roosevelt took office in 1933, promising a “New Deal” for the American people. This ambitious program encompassed a wide array of initiatives, prioritizing economic recovery, job creation, and social reform. The Hundred Days, a period early in Roosevelt’s presidency marked by a flurry of legislative activity, set the groundwork for sweeping reforms. Key measures included the establishment of the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC), which provided jobs for young men in public works projects, and the Public Works Administration (PWA), aimed at large-scale infrastructure development to stimulate employment.
The New Deal also significantly altered the landscape of financial regulation. The Banking Act of 1933, which established the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), helped restore public confidence in the banking system by insuring deposits. This was crucial in preventing further runs on banks and fostering stability. Additionally, the Securities Act of 1933 instituted regulations on the stock market, aimed at curbing the reckless speculation that contributed to the financial crisis.
Furthermore, agricultural programs like the Agricultural Adjustment Administration (AAA) sought to address the struggles facing farmers by instituting measures to reduce crop production and stabilize prices. While these initiatives were often controversial, they aimed to mitigate the plight of rural America during a tumultuous time in agricultural history.
In addition to economic measures, the New Deal initiated significant social reforms, particularly the establishment of social safety nets. The creation of the Social Security Act in 1935 laid the foundation for a system that would provide financial assistance to retirees, the unemployed, and those with disabilities. This marked a critical shift towards a more welfare-oriented state, reshaping America’s social contract with its citizens.
Despite substantial efforts, the New Deal faced criticism from various quarters. Some believed that Roosevelt’s measures did not go far enough to support struggling individuals and communities, while others argued that the interventionist approach expanded government power disproportionately. Detractors included both conservatives fearing an encroachment upon capitalistic principles and leftist groups demanding more radical reforms.
The multifaceted response to the Great Depression not only sought to rebuild the economy but also spurred a cultural shift in attitudes towards government intervention. The lessons learned from this period influenced future policies and established a legacy of federal involvement in economic and social welfare that persists to this day.
Long-Term Impact and Great Depression’s Lessons Learned
The Great Depression fundamentally reshaped the American economic landscape and has had lasting implications for the world. The struggles and reforms of this era laid the foundations for contemporary economic policies and political ideologies. The lessons learned during this tumultuous period have provided valuable insights into the complexities of managing economic crises and the necessity of resilience in the face of adversity.
One of the most significant long-term impacts of the Great Depression was the redefinition of the role of the federal government in the economy. The New Deal established a precedent for large-scale government intervention to address economic challenges. Policymakers began to understand that unregulated capitalism could lead to devastating consequences, and thus a balance was needed between market forces and government oversight. The establishment of regulatory bodies, like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the FDIC, ensured that safeguards were put in place to protect against future financial catastrophes.
Moreover, the social safety nets created during the New Deal, including Social Security and unemployment insurance, have become permanent fixtures within the American social welfare system. These programs represent a commitment to the well-being of citizens in times of crisis, offering a measure of economic security that had been previously absent. The collective understanding of the government’s responsibility to care for its citizens during economic downturns continues to influence political discussions about the role of social welfare today.
The Great Depression also catalyzed social movements advocating for civil rights and labor reforms. The economic struggles experienced by marginalized populations highlighted systemic inequalities that needed addressing, sowing seeds for the civil rights movements in subsequent decades. Labor unions gained strength during the Depression, advocating for workers’ rights and better conditions. This shift towards organized labor would reshape workplace regulations and usher in significant reforms aimed at protecting workers.
Additionally, the Great Depression taught lessons about the interconnectivity of global economies. The protectionist measures that followed the initial crash, such as high tariffs, created a ripple effect that exacerbated global economic challenges. The experience highlighted the necessity of international cooperation and coordination in resolving economic issues, emphasizing that isolated actions can lead to broader, unintended consequences.
Finally, the lessons of the Great Depression resonate in contemporary economic discourse. The importance of crisis management, timely federal intervention, and the protection of vulnerable populations remain pivotal themes in national and global economic policies. The economic downturn of 2008, often compared to the Great Depression, underscored the ongoing relevance of these historical lessons and the need for vigilance against economic pitfalls.
In conclusion, the legacy of the Great Depression shaped not only the policies of the United States but also the ways in which societies around the world address economic crises. The insights gained from this era serve as an essential reminder of the importance of adaptability, cooperation, and compassion in navigating challenges that affect the economic landscape. For more about the lessons from the Great Depression read also our article The Great Depression: Lessons from the Economic Catastrophe of 1929.
Conclusion
The Great Depression stands out as a pivotal moment in history that reshaped the economic, social, and political dimensions of American life. The complex interplay of causes leading to the collapse, the profound economic consequences, and the lasting impacts on society illustrate the depth of this historical crisis. Through examining the governmental responses and the lessons learned, we see how transformative this era was for American policy and public perception.
The challenges faced during the Great Depression still resonate today, shaping contemporary discourse concerning economic stability, welfare, and government intervention. The enduring legacy of this period serves as a testament to human resilience and adaptability in the face of tremendous adversity. As we reflect on the lessons of the Great Depression, it becomes evident that understanding the past is crucial in forging a path towards a more equitable and prosperous future.